Through an international collaboration, using breast cancer as a biological paradigm, Flavio Maina Team publishes a work in the Theranostics journal exemplifying how specificity in targeting cell cycle regulators is essential for combinatorial cancer therapies.
BCL-XL BLOCKAGE IN TNBC MODELS CONFERS VULNERABILITY TO INHIBITION OF SPECIFIC CELL CYCLE REGULATORS
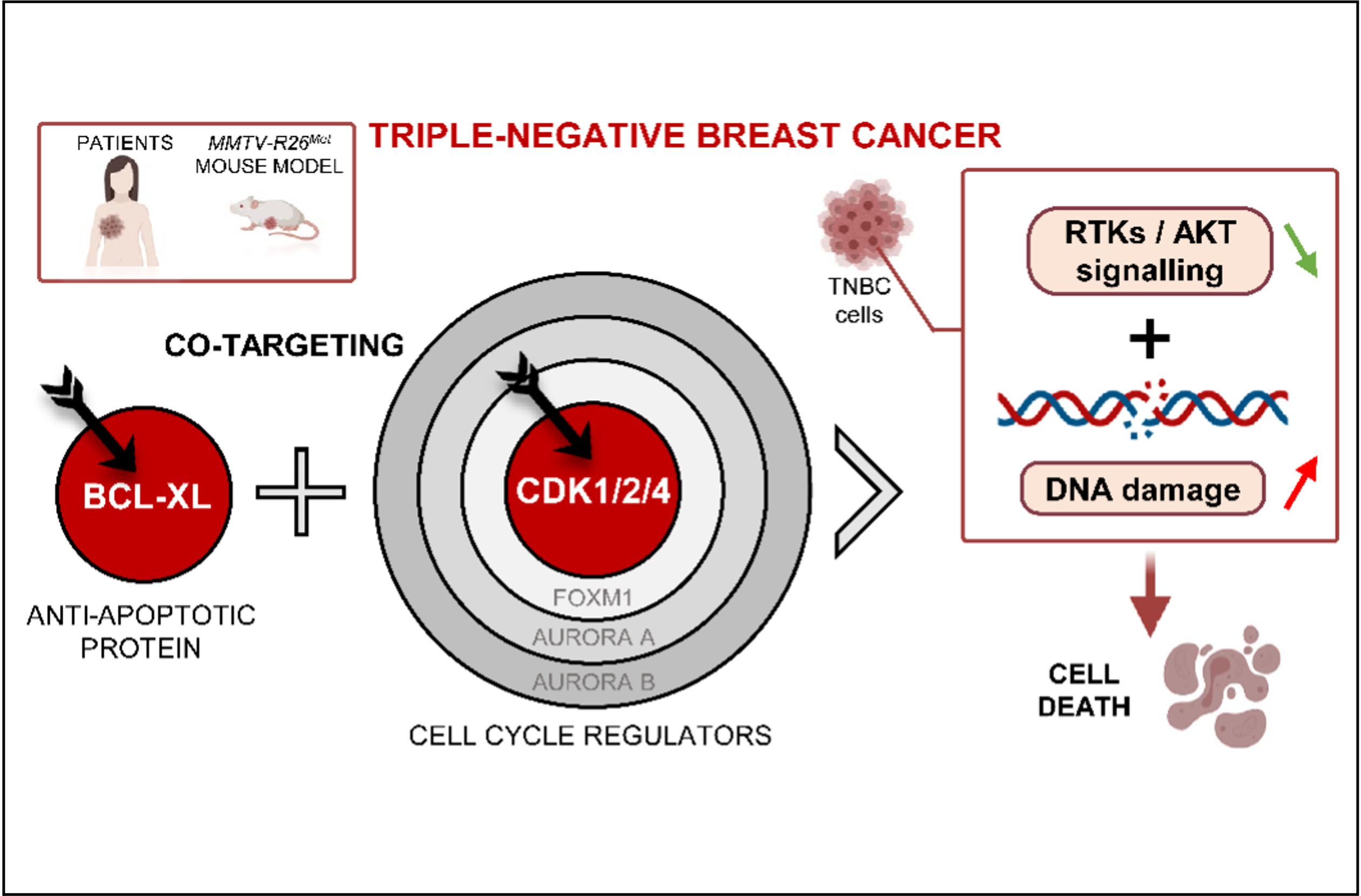
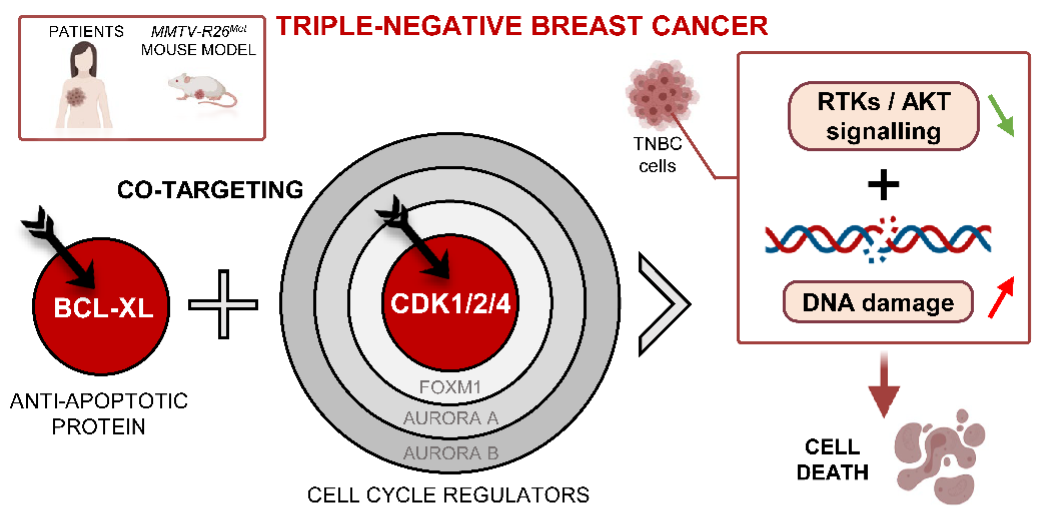
Cell cycle regulators are frequently altered in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC), a highly aggressive breast cancer subtype with very limited therapeutic options due to high inter- and intra-tumour heterogeneity, and significant resistance to currently proposed treatments. Emerging agents targeting these signals offer the possibility of designing new combinatorial therapies.
F. Maina’s team has shown that high expression levels of both the gene encoding BCL-XL (anti-apoptotic protein) and specific cell cycle regulators correlate with poor survival outcomes of TNBC patients. A mouse line modelling TNBC was recently generated by the authors (Lamballe et al., Adv Sci 2020). This new mouse model allowed them to demonstrate that blocking BCL-XL confers vulnerability to drugs targeting cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK1/2/4), but not to those targeting other cell cycle regulators, such as FOXM1, CDK4/6, Aurora A and Aurora B, in all TNBC cell lines (mouse and human) tested. Combined blockage of BCL-XL and CDK1/2/4 interfered with tumour growth in vivo.This work shows that co-targeting of BCL-XL and CDK1/2/4 acts synergistically to significantly reduce TNBC cell viability. Mechanistically, this co-targeting results in the combined depletion of survival and receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)/AKT signals, and the concomitant restoration of the FOXO3a tumour suppressor functions. This is accompanied by an accumulation of DNA damage and consequently apoptosis.
This study illustrates the possibility of exploiting the vulnerability of TNBC cells to CDK1/2/4 inhibition by targeting BCL-XL. Furthermore, it underlines that specificity matters in targeting cell cycle regulators for combinatorial anticancer therapies.
To know more :
- BCL-XL blockage in TNBC models confers vulnerability to inhibition of specific cell cycle regulators
Olivier Castellanet1,6, Fahmida Ahmad1,6, Yaron Vinik2, Gordon B. Mills3, Bianca Habermann1, Jean-Paul Borg4,5, Sima Lev2, Fabienne Lamballe1,7, Flavio Maina1,7
Theranostics 2021; 11(19): 9180-9197. doi:10.7150/thno.60503
Contact
Fabienne Lamballe – fabienne.lamballe@univ-amu.fr
Flavio Maina – flavio.maina@univ-amu.fr