Maina Team publishes in Journal of Hepatology.
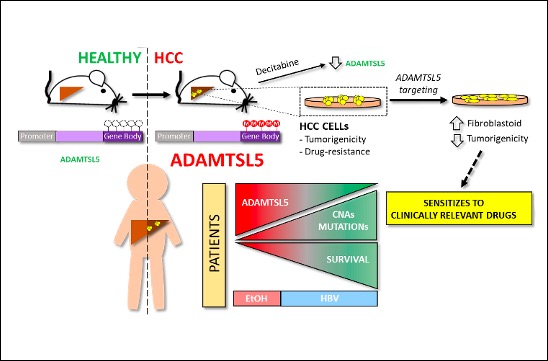
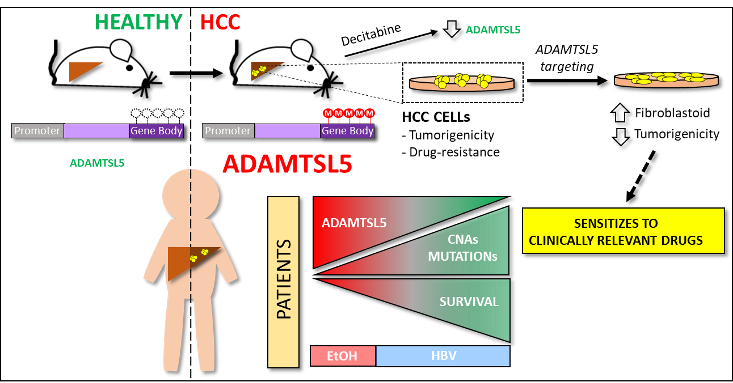
The tumour microenvironment has profound effects on cancer initiation, progression and drug resistance. ADAMTSL5 is a protein secreted by HCC cells, not previously linked to cancer. We found that ADAMTSL5 is an epigenetically activated oncogene overexpressed in a large fraction of human HCC patients and in HCC mouse models. We demonstrated that ADAMTSL5 is implicated not only in tumorigenesis, but also in drug resistance, as ADAMTSL5 targeting confers sensitivity to drugs used in the clinic.
ADAMTSL5 is an epigenetically activated gene underlying tumorigenesis and drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
Summary. The tumour microenvironment shapes tumour growth through cellular communications that include both direct interactions and secreted factors. The aim of this study was to characterize the impact of the secreted glycoprotein ADAMTSL5, whose role in cancer has not been previously investigated, on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methylome analysis revealed hypermethylated gene body CpG islands at the ADAMTSL5 locus in both mouse and human HCC, correlating with higher ADAMTSL5 expression. ADAMTSL5 targeting interfered with tumorigenic properties of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo, whereas ADAMTSL5 overexpression conferred tumorigenicity to pre-tumoral hepatocytes sensitized to transformation by a modest level of MET receptor expression. Mechanistically, ADAMTSL5 abrogation led to reduction of several oncogenic inputs relevant to HCC, including reduced expression and/or phosphorylation levels of receptor tyrosine kinases MET, EGFR, PDGFRβ, IGF1Rβ, or FGFR4. This phenotype was associated with significantly increased sensitivity of HCC cells to clinically relevant drugs, namely Sorafenib, Lenvatinib, Regorafenib. Moreover, ADAMTSL5 depletion drastically increased expression of AXL, accompanied by a sensitization to Bemcentinib. Our results point to a role for ADAMTSL5 in maintaining the function of key oncogenic signalling pathways, suggesting that it may act as a master regulator of tumorigenicity and drug resistance in HCC.
To know more :
Journal of Hepatology 2020 Nov 13;S0168-8278(20)33758-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.11.008.
Maria Arechederra1, Sehrish K Bazai1, Ahmed Abdouni1, Celia Sequera1, Timothy J Mead2, Sylvie Richelme1, Fabrice Daian1, Stéphane Audebert3, Rosanna Dono1, Anthony Lozano4, Damien Gregoire4, Urszula Hibner4, Daniela S Allende5, Suneel S Apte2, Flavio Maina6
1 Aix Marseille Univ, CNRS, Developmental Biology Institute of Marseille (IBDM), UMR7288, Parc Scientifique de Luminy, Marseille (France).
2 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland, OH 44195 (USA).
3 Aix-Marseille Univ, CRCM, Marseille Proteomics, INSERM, CNRS, Institut Paoli-Calmettes, Marseille, France.
4 Institut de Génétique Moléculaire de Montpellier, Univ Montpellier, CNRS, Montpellier, France.
5 Pathology Department, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, 44195 (USA).
6 Aix Marseille Univ, CNRS, Developmental Biology Institute of Marseille (IBDM), UMR7288, Parc Scientifique de Luminy, Marseille (France).
Contact
Flavio Maina – flavio.maina@univ-amu.fr